NanoPhoton 面掃描共聚焦拉曼系統 |
|
Raman microscope with ultra-high speed imaging capability 去NanoPhoton網站了解更多 Features
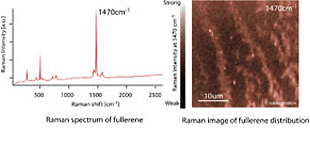
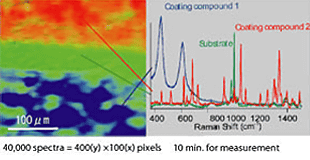
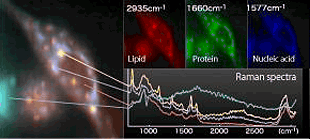
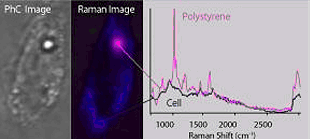
Outline of RAMAN-11RAMAN-11 is a next generation laser microscope observing an
image of a sample with Raman scattering lights emitted from the molecules. Raman
spectroscopy technique used for RAMAN-11 gives researchers the knowledge for the
details of constituent elements of organelles or protein. By observing the Raman
scattering lights emitted from the molecules of the living cells, distribution
of the molecules can be imaged with the colors (wavelength) unique to those
molecules without using the staining method. Examples of observation
NanoPhoton 三維掃描共聚焦拉曼系統
Nonophoton's Laser Raman Microscope took a large step as RAMANplus. The RAMANplus has a built-in video rate confocal reflection system that acquires the three-dimensional surface profile very fast in advance of Raman measurenment. After the Raman measurement, the RAMANplus automatically appends the Raman chemical information to the three-dimensional profile. 去NanoPhoton網站了解更多 Features
Technologies
Observation example of Diamond file
The reflected light confocal observation gives the precise extended focus reflected image (grey color). The Raman observation gives the data of the crystal quality. These data are acquired and overlaid automatically. |
|
上海玻色智能科技有限公司 上海: (021)3353-0926, 3353-0928 北京: (010)8217-0506 廣州: 139-0221-4841 武漢: 139-1733-4172 全國銷售服務熱線:4006-171751 Email: info@bosontech.com.cn m.healthyfitnesstip.com 2008-2022 All Rights Reserved! |
|

 線陣CCD光纖光譜儀
線陣CCD光纖光譜儀